Versatility and Benefits of 1031 Exchanges in Real Estate Investing
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding 1031 Exchanges
- Tax Advantages and Implications
- Requirements for a Successful 1031 Exchange
- How 1031 Exchanges Stimulate Growth
- Real-Life Examples of 1031 Exchanges
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion
Introduction
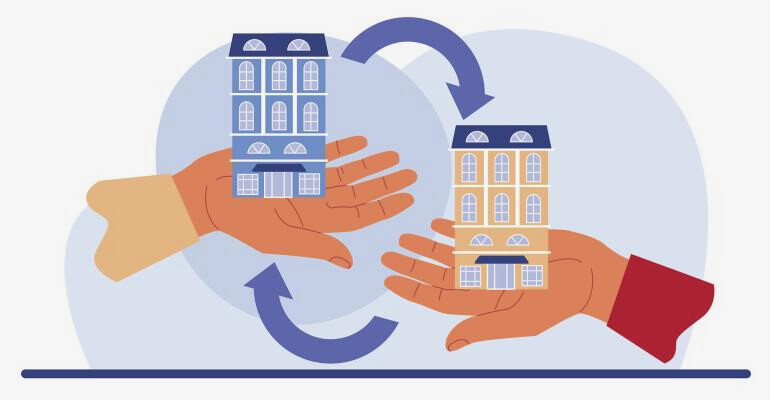
In the dynamic world of real estate investing, 1031 exchanges stand out as a pivotal strategy for investors looking to maximize their gains while deferring taxes. Named after Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code, these exchanges provide a legal route to defer paying capital gains taxes when swapping investment properties. This offers savvy investors a unique opportunity to reallocate capital without the immediate tax hit, making it a compelling option for those keen on expanding or refining their real estate portfolios. This article delves into the versatility and benefits of 1031 exchanges, offering insights into how they can be leveraged for optimal financial outcomes.
Understanding 1031 Exchanges
A 1031 exchange is a strategy that allows for the deferral of capital gains taxes on investment properties when these properties are exchanged for ‘like-kind’ assets. In an arena where strategic financial management is key, resources such as 1031 Pros offer invaluable guidance, helping novice and seasoned investors navigate the nuances of these exchanges. This concept is not new; it has roots that date back to the early 20th century. The idea was formalized to promote reinvestment in business or investment properties, which, in turn, stimulates economic growth. Unlike a simple sale that triggers immediate tax liabilities, a 1031 exchange adheres to strict regulations but offers the advantage of postponing tax payments. The properties involved must be alike in nature or character, though not necessarily in grade or quality. As the approach evolves, so does the complexity of understanding and applying the rules effectively, making it crucial for investors to remain well-informed and diligent in their application.
Tax Advantages and Implications
The tax deferral benefits of a 1031 exchange are the most enticing aspect for investors. By deferring capital gains taxes, investors retain a more significant portion of their capital, which can be reinvested to acquire higher-value properties, thus potentially amplifying their investment returns over time. To illustrate, consider an investor who, through a 1031 exchange, manages to transfer equity from a single-family rental home to a multi-family complex or a commercial property. This maneuver defers a significant tax expense and enhances the investor’s asset base and income potential for those looking to delve deeper into strategic tax management within the real estate; tax strategies in real estate offer comprehensive guidelines and insights.
Requirements for a Successful 1031 Exchange
Executing a 1031 exchange successfully requires adherence to a series of specific criteria. The first critical factor is ensuring that the properties exchanged are classified as ‘like-kind.’ This broad definition encompasses various properties, from residential and commercial to industrial, provided they are held for investment or productive use in a business. Timeliness is another indispensable requirement. Investors are given 45 days to identify potential replacement properties and must complete the exchange within 180 days of selling the initial property. Furthermore, the transaction must be facilitated through a qualified intermediary to comply with IRS regulations. Navigating these intricacies demands precise planning and expert advice, emphasizing the importance of detailed preparation when considering this strategy.
How 1031 Exchanges Stimulate Growth
Beyond individual financial gain, 1031 exchanges have broader implications for market growth and economic stimulation. By enabling investors to shift capital more freely, these exchanges promote liquidity and allow investment in higher-value or strategically located properties. This continual reinvestment boosts demand across various market segments, encouraging construction, development, and revitalizing underperforming areas. For instance, investors often leverage 1031 exchanges to diversify portfolios and enter burgeoning real estate markets poised for growth. These actions not only bolster individual portfolios but also contribute significantly to the overall dynamism of the real estate market. An examination of recent trends in the real estate market underscores the significant effect of investment fluidity sparked by 1031 exchanges.
Real-Life Examples of 1031 Exchanges
Consider the story of an investor who transitioned from owning multiple single-family rental properties to acquiring a large commercial property through a 1031 exchange. By deferring substantial capital gains taxes, this investor could retain and redirect capital that facilitated the purchase of a property with higher return potential and greater cash flow. Another example involves a small business that sold its custom facility to move into a new space that increased operational efficiency. The 1031 exchange allowed this business to upgrade its premises without the immediate financial strain of tax liabilities, illustrating the strategy’s flexibility and applicability across different investment scenarios.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Despite the clear advantages, the success of a 1031 exchange can be jeopardized by common missteps. Adherence strictly to the identification and exchange deadlines is a frequent error that can disqualify an exchange. Overlooking the necessity of using a qualified intermediary or misunderstanding the definition of like-kind properties can also derail the process. Investors must ensure compliance with IRS guidelines and seek professional advice to navigate these complexities effectively. Proper education and meticulous planning are crucial to avoid these pitfalls and to execute a seamless 1031 exchange that meets all regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 1031 exchanges are a powerful tool for real estate investors seeking to expand and optimize their portfolios while deferring tax liabilities. The intricate nature of these exchanges necessitates careful planning, adherence to strict timelines, and compliance with regulatory requirements. With the right approach, investors can harness the full potential of 1031 exchanges, unlocking opportunities for significant growth and diversification. By leveraging the expertise of professional advisors and staying informed on market trends, investors can confidently navigate the complexities of the real estate landscape and maximize their financial outcomes.
You may also read: “Maximizing Productivity in Small Offices with Compact Standing Desks”