How to Integrate Zero Trust Security with Your Existing IT Infrastructure
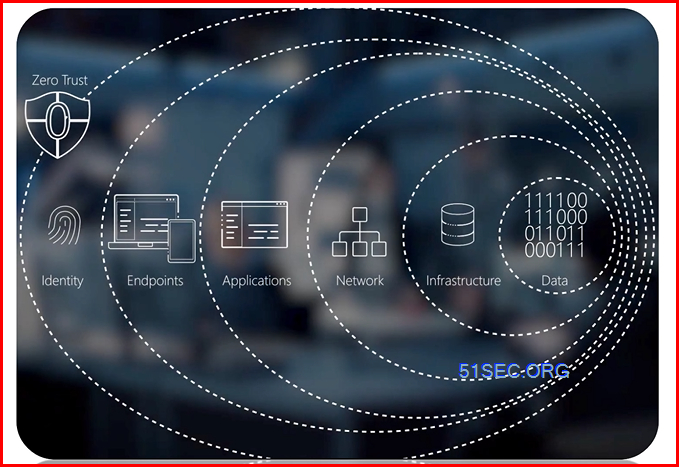
In today’s fast-changing cyber threat landscape, organizations must constantly enhance their security strategies to combat increasingly sophisticated attacks. Unlike traditional security models that depend on a trusted network perimeter, Zero Trust acknowledges that threats can arise both within and outside the network. Therefore, it is crucial to rigorously authenticate and authorize every user, device, and application requesting access to organizational resources.
Integrating Zero Trust Security into your IT infrastructure may initially seem daunting, but it is a crucial step in fortifying your organization’s cybersecurity posture. As remote work, cloud computing, and IoT devices proliferate, the relevance of the traditional network perimeter diminishes. Zero Trust provides a comprehensive approach to ensure that access to critical data and applications is monitored meticulously and continuously. Consult with IT Support Los Angeles experts to harness the power of zero trust security for business IT infrastructure.
In this article, we will explore what is zero trust security and ways to integrate zero trust security.
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero-trust security is a cybersecurity model grounded in strict access controls that do not automatically trust any user or device, regardless of their location within the network. In a zero-trust framework, every user and device, including those already inside the network, must be verified and authenticated before accessing any resources.
This approach helps minimize the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access by continuously verifying trust levels through various security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and least privilege access policies. By implementing Zero-Trust Security principles, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and better protect against evolving cyber threats in today’s digital landscape.
8 Ways to Integrate Zero Trust Security
- Assess Your Current Infrastructure
Before implementing Zero Trust security measures, it is crucial to assess your current infrastructure thoroughly. This assessment should include a comprehensive review of all existing network components, user access controls, and data flow within the organization.
Understanding your current setup can identify potential vulnerabilities or weak points that need to be addressed when transitioning to a Zero-Trust model. Additionally, evaluating your infrastructure allows you to determine the level of effort and resources required for a successful implementation. Conducting a detailed assessment is an essential first step in integrating Zero-Trust security effectively within your organization.
- Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implementing Identity and Access Management (IAM) is crucial in integrating Zero Trust Security into your organization’s cybersecurity framework. IAM systems help verify users’ identities and manage their access to sensitive data and resources within the network.
By implementing IAM protocols, organizations can enforce strict controls over user permissions and ensure that only authorized individuals have access to specific assets. This not only enhances security measures but also helps in preventing unauthorized access or potential breaches. Integrating IAM as part of a comprehensive Zero Trust Security strategy can significantly strengthen your overall cybersecurity posture and safeguard your digital assets from potential threats.
- Micro-segmentation and Network Controls
As businesses increasingly prioritize cybersecurity, integrating Zero Trust Security measures like micro-segmentation and network controls has become crucial. Micro-segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller segments to limit lateral movement for potential attackers, enhancing overall security.
Network controls, on the other hand, enforce policies that dictate which users and devices can access specific parts of the network, further strengthening defenses. By partnering with the Managed IT Services Los Angeles team, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface and bolster their overall cybersecurity posture in an increasingly volatile digital landscape.
- Adopt Device and Endpoint Security
Adopting device and endpoint security is a critical step in integrating zero-trust security into your organization’s cybersecurity framework. By implementing stringent measures to secure devices and endpoints, such as desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and servers, you can establish a strong foundation for a zero-trust architecture.
This involves implementing access controls, encryption, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and regularly monitoring device health and activity. By fortifying the security of these entry points into your network, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and potential breaches, enhancing your overall security posture in alignment with zero-trust principles.
- Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis
Network traffic monitoring and analysis are crucial components of implementing a Zero-Trust security model. By continuously monitoring network traffic, organizations can gain visibility into all network activities, allowing them to identify potential threats and anomalies in real-time.
Analysis of this monitored traffic enables organizations to detect unauthorized access attempts, unusual behavior patterns, and other indicators of compromise. By leveraging advanced analytics tools and technologies, organizations can enhance their ability to detect and respond to security incidents promptly, thereby strengthening their overall security posture in line with the Zero Trust principles.
- Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Continuous monitoring and incident response are crucial when integrating Zero Trust security into an organization’s cybersecurity framework. Continuous monitoring involves real-time assessment of network traffic, user behavior, and access patterns to identify any anomalies or potential security threats promptly.
This proactive approach allows for the early detection of unauthorized activities and helps prevent breaches before they escalate. A robust incident response plan is essential to address security incidents effectively and minimize their impact on the organization. By combining continuous monitoring with a well-defined incident response strategy, businesses can enhance their security posture and mitigate risks in an evolving threat landscape.
- Third-Party Access Control
When implementing a zero-trust security model, managing third-party access control is a critical aspect that organizations must address. Third-party vendors and partners often require access to internal systems and data, making them potential entry points for cyber threats.
Organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches by enforcing strict access controls for third parties, such as requiring multi-factor authentication, limiting privileges based on specific needs, and monitoring their activities closely. Implementing robust third-party access control measures is essential in maintaining a secure environment within the framework of Zero Trust security principles.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) is a critical component of implementing Zero-Trust Security within an organization. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, UEBA solutions can monitor and analyze the behavior of users and entities within the network in real time.
This enables organizations to detect anomalies, unusual patterns, or potential security threats that traditional security measures may overlook. UEBA provides valuable insights into user activities, helping organizations promptly identify and respond to potential security incidents. By integrating UEBA into their Zero Trust framework, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and better protect their sensitive data and resources from evolving cyber threats.
Conclusion
Integrating Zero Trust Security into your IT infrastructure is a vital step in strengthening your organization’s cybersecurity. By adopting Zero Trust principles, you enhance your defenses against cyber threats and promote a culture of continuous vigilance and verification. Though the transition may pose challenges, the long-term benefits of improved security and compliance are significant. With careful planning, the right technologies, and a focus on ongoing education, your organization can successfully navigate this change and build a robust security posture. Embracing Zero Trust Security will safeguard your assets and position your organization as a leader in cybersecurity.