The Role of Prototyping in Metal Fabrication and Design
Machining and fabrication have evolved significantly from traditional methods. Modern metal machining now follows a more streamlined process—design, prototyping, and fabrication. Prototyping plays a crucial role in this workflow, serving as the key phase where designers can test and validate their concepts. It allows for the exploration of the most effective manufacturing techniques, and any issues identified during this stage are fed back into the design process for refinement and improvement.
Clarification of Process Flow
In metal fabrication and design, the process flow typically begins with the conceptualization and creation of a detailed design. Once the design is established, prototyping services come into play to transform these digital concepts into tangible models. This critical phase allows designers and engineers to evaluate the design’s functionality, aesthetics, and feasibility in real-world conditions. Through prototyping, manufacturers can assess whether the design meets the desired specifications or if adjustments are necessary before full-scale production. This stage is essential for identifying potential design flaws early, preventing costly errors in later stages.
For example, if you were designing an aluminum bracket, you would first use CNC machining to verify the accuracy and strength. At the same time, you would investigate laser cutting. Having investigated material removal rates, costs, and process precision, you can choose an approach that is faster, and more cost-effective.
Prototyping services play a pivotal role in facilitating this cycle, providing invaluable insights that guide the transition from concept to finished product. By integrating prototyping early in the design process, manufacturers can streamline production and reduce the risks associated with launching a new metal fabrication project.
Validation and Testing of Theoretical Designs
Designs are often built using relational equations and standards. Prototypes solve this problem by allowing you to test designs under realistic conditions before moving to large-scale production.
Virtual Prototyping
One way to prototype is virtually – creating a 3D model of the design and simulating it. You can test for deformation, stress endurance, or other conditions that would affect its performance. This is done using various CAD and simulation software. For instance, finite element analysis (FEA) on ANSYS or SolidWorks can help predict how a part will behave under different loads.
Physical Prototypes
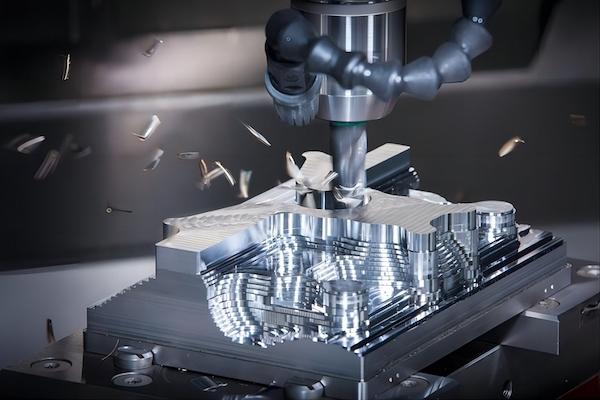
The next step is creating a physical prototype. This gives a tangible model to explore real-world challenges and perform practical tests. CNC machining is one approach, particularly suitable for metal parts where precision is important. For rapid prototyping, 3D printing can be used. This method is helpful for designs that need faster iterations or non-metal materials.
Cost Reductions
Prototyping services play a significant role in reducing costs throughout the metal fabrication and design process. By creating prototypes before full-scale production begins, companies can identify design flaws and manufacturing inefficiencies early on, avoiding expensive revisions later. This allows for testing and fine-tuning the design without committing to large-scale production runs, which can be costly if the design turns out to have critical errors.
The ability to spot and resolve potential issues at the prototyping stage ensures that manufacturers don’t waste time or resources on faulty products, leading to significant cost savings in the long run.
In addition to reducing the risk of costly errors, prototyping services help streamline the production process, further driving down expenses. By simulating the final product through prototypes, manufacturers can optimize machining methods and materials, selecting the most cost-effective solutions without compromising quality. This early stage validation not only reduces the likelihood of rework but also ensures that the manufacturing process will be as efficient as possible when scaling up.
Ultimately, investing in prototyping services can lead to a more economical approach to metal fabrication, resulting in a faster time to market and reduced overall production costs.
Applications Across Metal Fabrication Industries
The prototyping practice is followed in multiple metal fabrication industries, particularly, the automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors. Some examples are presented for reference:
Automotive: Ducati, the renowned motorcycle manufacturer, utilizes Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) to prototype engine components. This approach lets them assess the design holistically. Another example is of car manufacturer, Ford. They have been consistently using 3D printing technologies to build prototypes to test and evaluate their new parts.
Aerospace: Bell Helicopter uses Laser Sintering and Fused Deposition Modeling in their Rapid Prototyping Lab. Boeing is one of the leading aerospace companies that rely extensively on prototyping for aircraft parts. The company has developed prototypes for the 787 Dreamliner using advanced composite materials.
Medical Devices: Stryker Corporation uses prototyping in titanium to create custom-fit orthopedic implants for joint replacement. Similarly, Medtronic applies metal prototyping in the design of surgical instruments and implantable devices, including stents and pacemakers.
Conclusion
Prototyping is fundamental to an efficient production line. It acts as a checkpoint that allows manufacturers to refine designs, processes, and costs before full-scale production.
You may also read: Impact of Maritime Law on Seafarers and Coastal Communities
As they identify flaws and optimize workflows early, it saves time and resources. Collectively, the physical and virtual aspects of prototyping ensure that the final product meets quality and performance standards.